This is the CO₂ footprint of your e-bike
Of course, e-bikes are more environmentally friendly than cars. They do not emit exhaust gases like a combustion engine, require less electricity to charge than an electric car and use fewer materials to build. It is not for nothing that e-bikes are an important building block in the Mobility transitionBut still, e-bikes also have nasty lithium-ion batteries built in. Just like electric cars, they don't directly contribute to environmental pollution, but they do cause emissions elsewhere – during battery production.
In general, the following applies: If you switch from a motorless “bio-bike” to an electric bike, your own Life cycle assessment. But if you switch from a car to an e-bike, you are doing something good for the environment. But what exactly does the CO₂ footprint of an e-bike really look like? We have done some research.
Federal Environment Agency analyses e-bike emissions
As a Evaluation of the Federal Environment Agency shows that the e-bike is one of the lowest-emissions modes of transport. Using an e-bike results in an average CO₂ emissions of approx. 3 g CO₂/passenger kilometre (Pkm). This is caused by electricity consumption and depends on the electricity mix used. In comparison, a car with a combustion engine emits around 166 g CO₂/Pkm, while public transport emits between 58 and 93 g CO₂/Pkm.4.
An e-bike produces about 263 kilos CO₂
Bosch / TÜV Rheinland
With 3 grams of CO2 per kilometer driven, the e-bike fares very well compared to other means of transport.
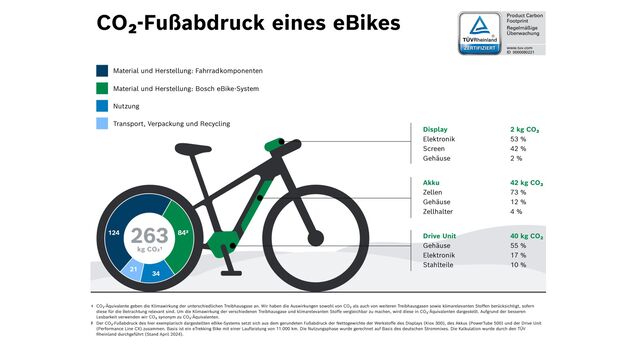
However, the CO₂ emissions from actual use do not yet include the Manufacturing the bike and the individual components. To this end, e-bike engine manufacturer Bosch 2024 has carried out an evaluation together with TÜV Rheinland. Over the entire service life, this results in a CO₂ footprint of an average of 263 kg CO₂ equivalentsFor comparison: This amount is also produced if you fly from Hamburg to Venice by plane.
E-bike emissions compared to electric cars
According to the Bosch study, a combustion engine car emits 166 grams of CO₂ per passenger kilometer, while an electric car emits 79 g CO₂/Pkm. This is many times more than the 3 g CO₂/Pkm of an e-bike. If you ride around 515 kilometers with an e-bike instead of a car with a combustion engine, the e-bike has already paid for itself in terms of CO₂ consumption, the study calculates.
Where do e-bike emissions come from?
The biggest environmental impact of e-bikes is, not surprisingly, the production of the battery. These are usually lithium-ion batteries, which contain cobalt, nickel, iron, copper, aluminum and lithium, among other things. The mining of these materials consumes large amounts of water, is associated with groundwater contamination and causes social and human rights problems.
Bosch / TÜV Rheinland
The CO2 footprint of the bike presented as an example by Bosch and TÜV Rheinland refers to an e-trekking bike with a mileage of 11,000 kilometers.
Bosch and TÜV Rheinland have also broken down exactly how materials contribute to the CO₂ footprint of an e-bike. The results of the CO2 analysis:
- Materials used, including battery: 79 percent
- Use: 13 percent
- Transport/Packaging/Recycling: 8 percent
If the components with about 84 kg CO₂ equivalents are considered individually, about 50 percent of the emissions are attributable to the battery48 percent on the DriveUnit and 2 percent on the Display.
Even seemingly small items play a role, such as the used Plastic partsAccording to its sustainability analysis, Bosch is using alternative materials for the cell holders, which make up the largest plastic part of the battery. However, if you own an e-bike and want to track these costs for your bike, it is difficult for most manufacturers.
What can you do to keep CO₂ consumption on e-bikes low?
The Federal Environment Agency has some tips on how e-bikers can optimize their environmental footprint.
- When buying new on longevity pay attention to both the battery and the wheel
- Bike and battery regularly waitto increase longevity
- E-Bike with green electricity load
- Disused but functional bikes resell
- Battery and wheel properly dispose
Around the lifespan of an e-bike battery, you should:
Conclusion: Great environmental potential despite CO₂ footprint
E-bikes have an environmental footprint of around 263 kg CO₂ over their entire lifespan. They emit 3 grams of CO₂ per kilometer driven. But despite these emissions, e-bikes have a great environmental potential: According to calculations by the Fraunhofer Institute Greenhouse gas emissions in Germany could be reduced by 34 percent by 2035 if the share of bicycle traffic were tripled.
